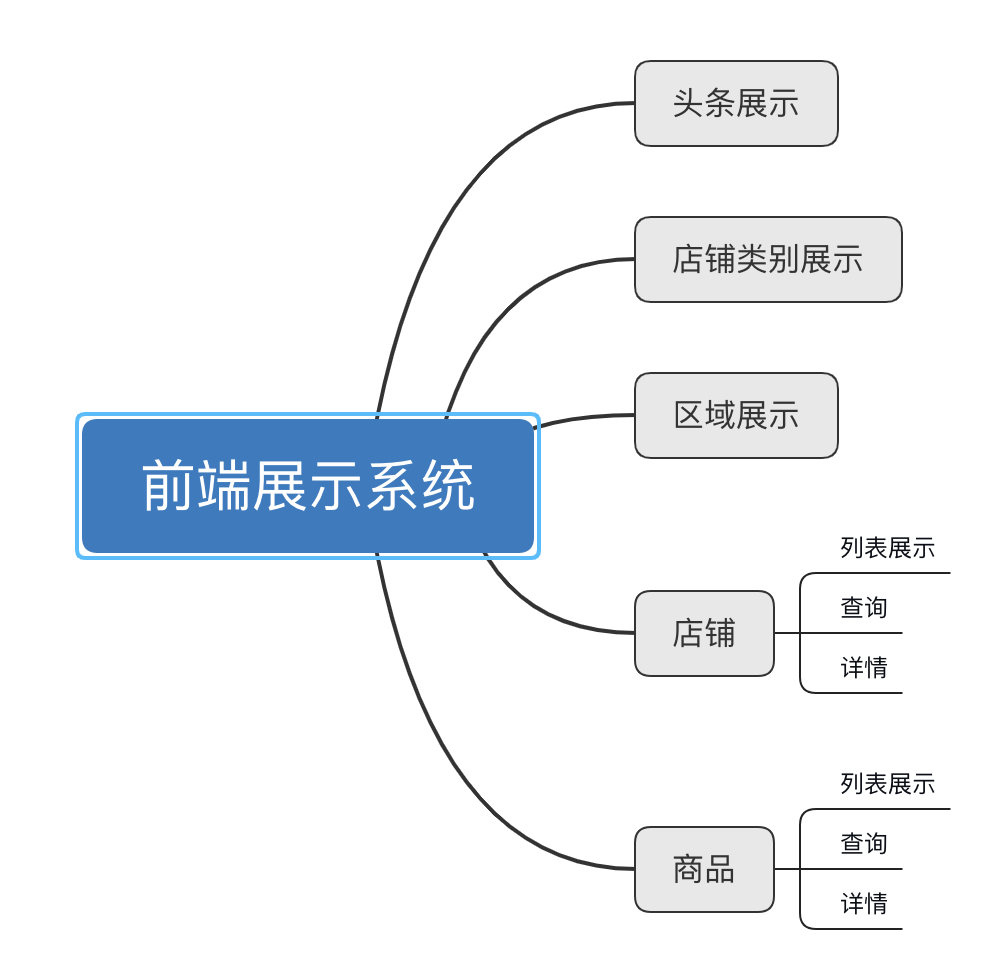
Notes of O2O projcet
Tech stack
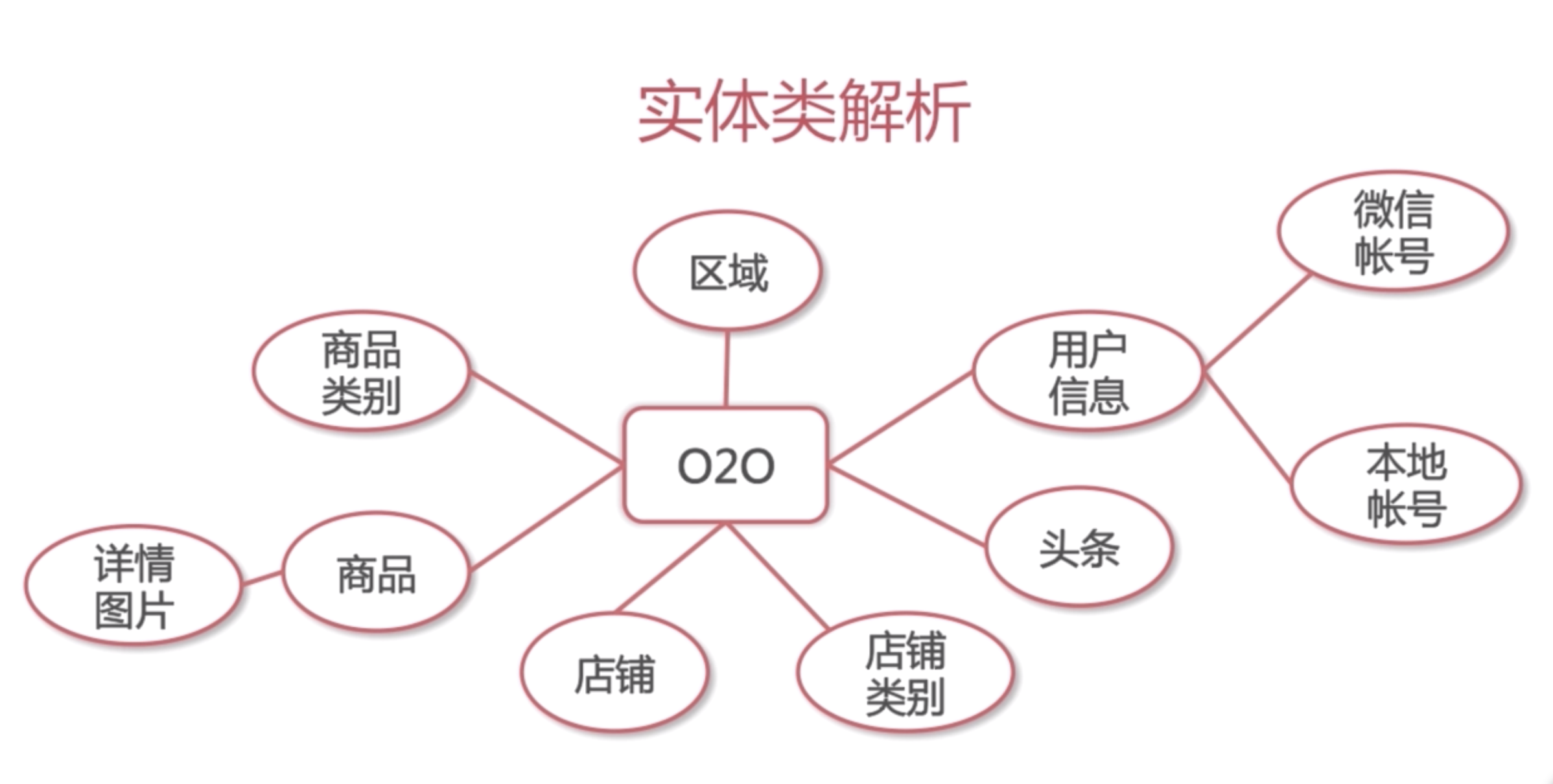
Shop
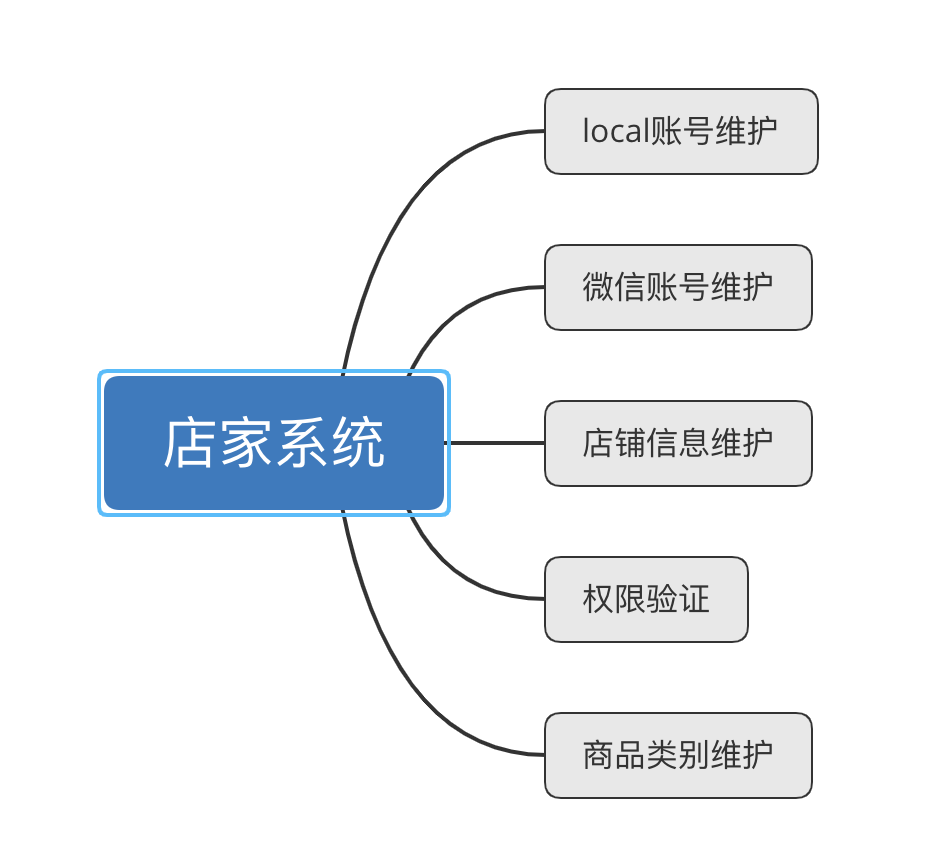
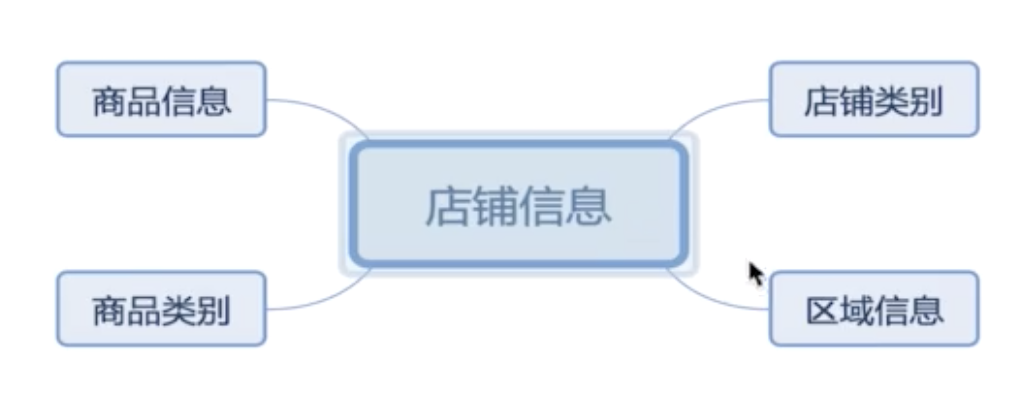
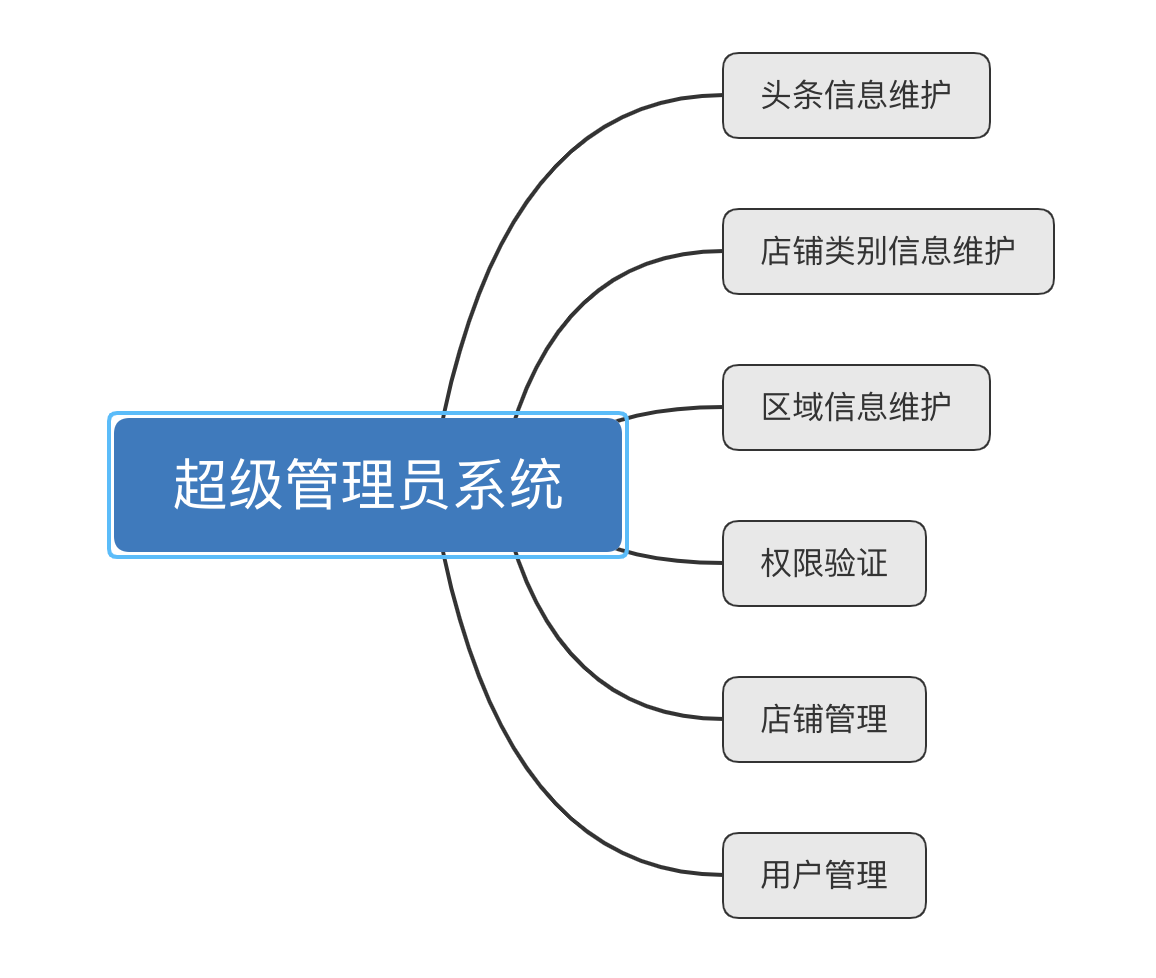
Administrator
Product
Concrete Class
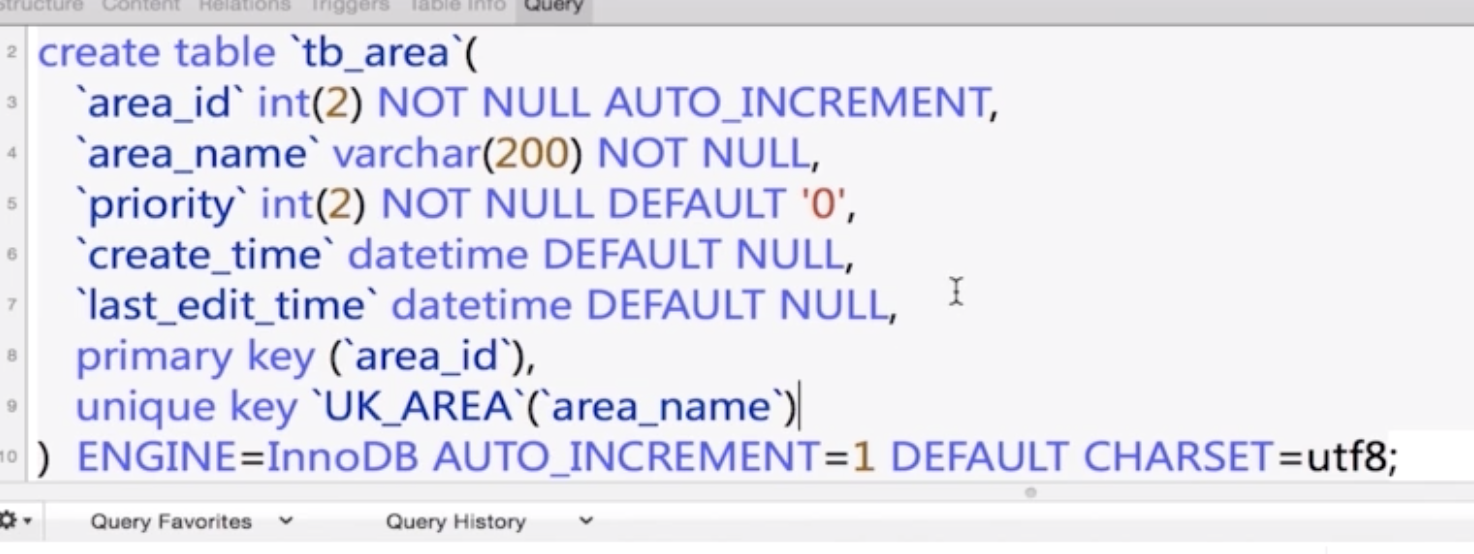
Area
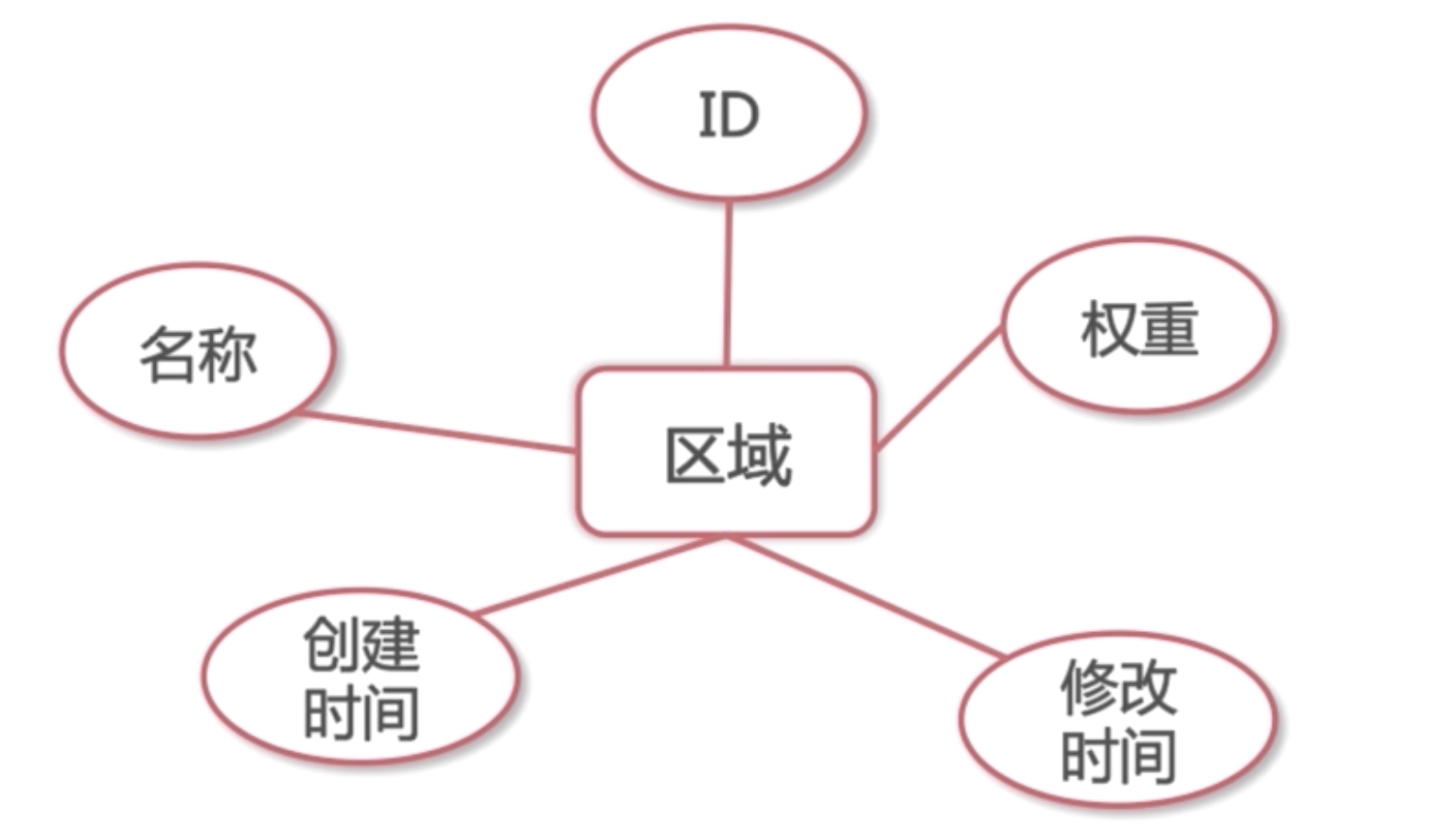
1. Build the class in Java
1. Build the table in database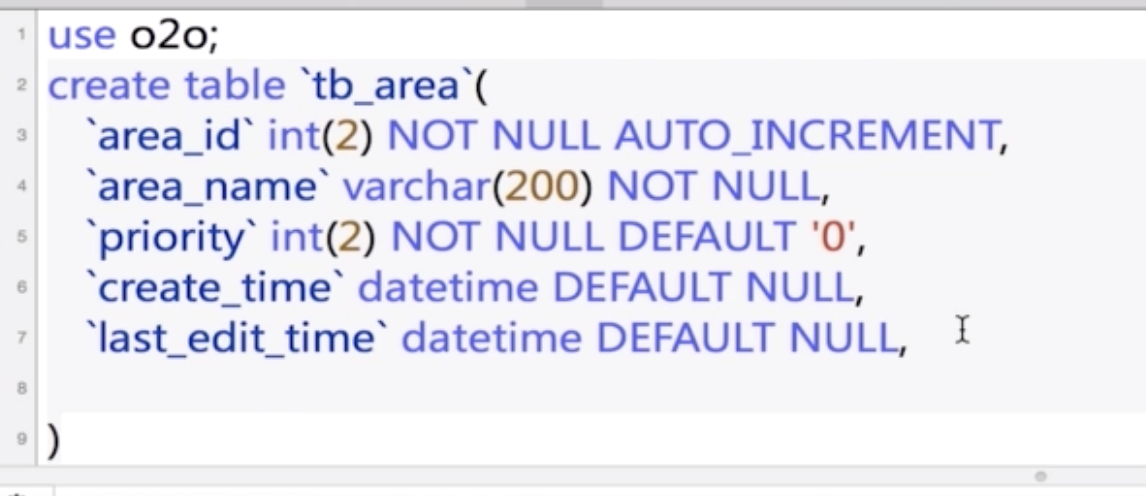
Q: Why do we use DateTime rather than TimeStamp in mySQL?
A: Because DateTime has a larger range of 0000 -> 9999 year, while TimeStamp can only varies between 1970 and 2037. However, TimeStamp can automatically adjust to the current time zone.
Q: What’s the difference between InnoDB and MYISAM?
A: MYISAM has a table lock that doesn’t allow multiple threads modifying the table while current thread working on it. InnoDB is locked by row. Also, MYISAM has a better read performance, while InnoDB has a better write performance.
PersonInfo
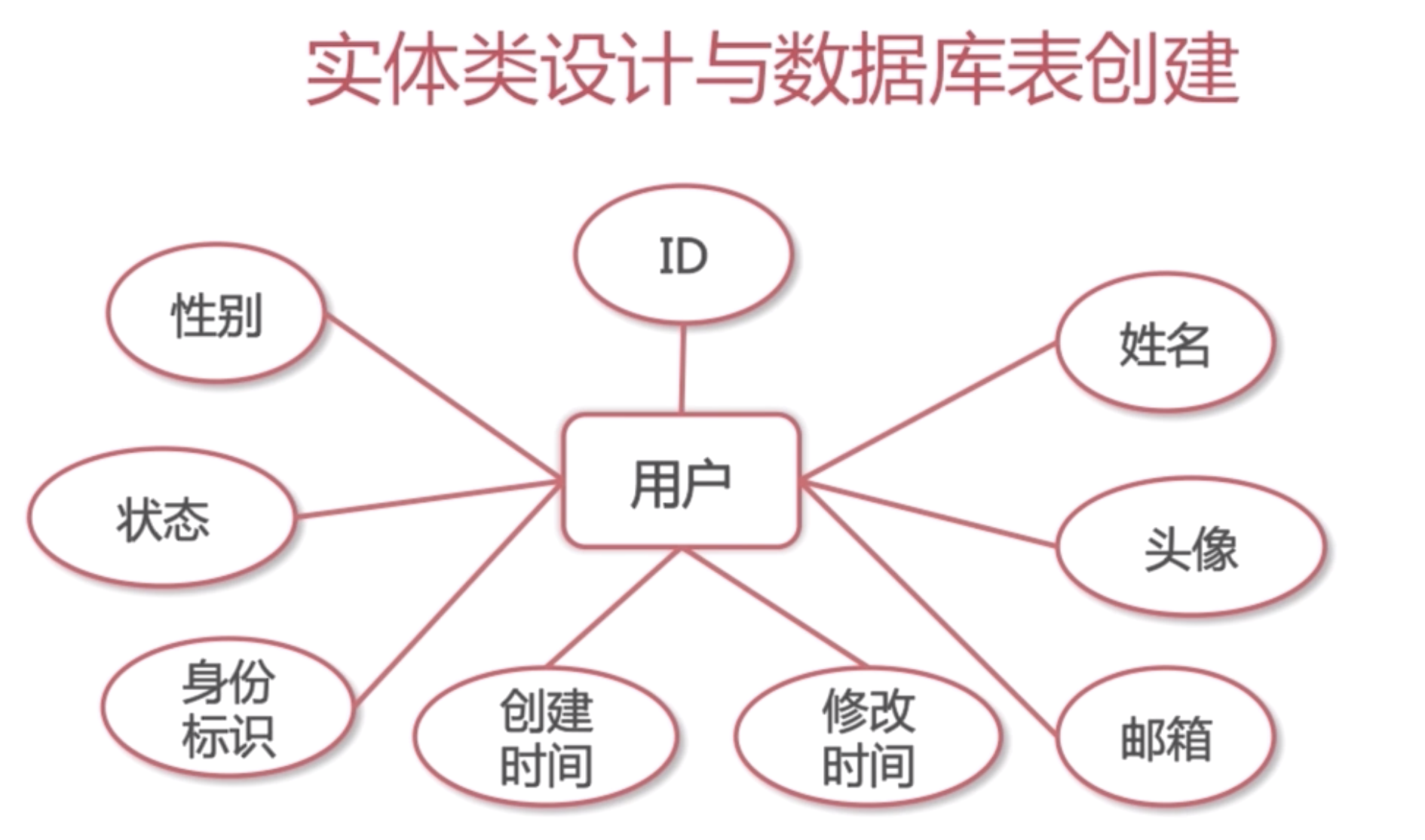
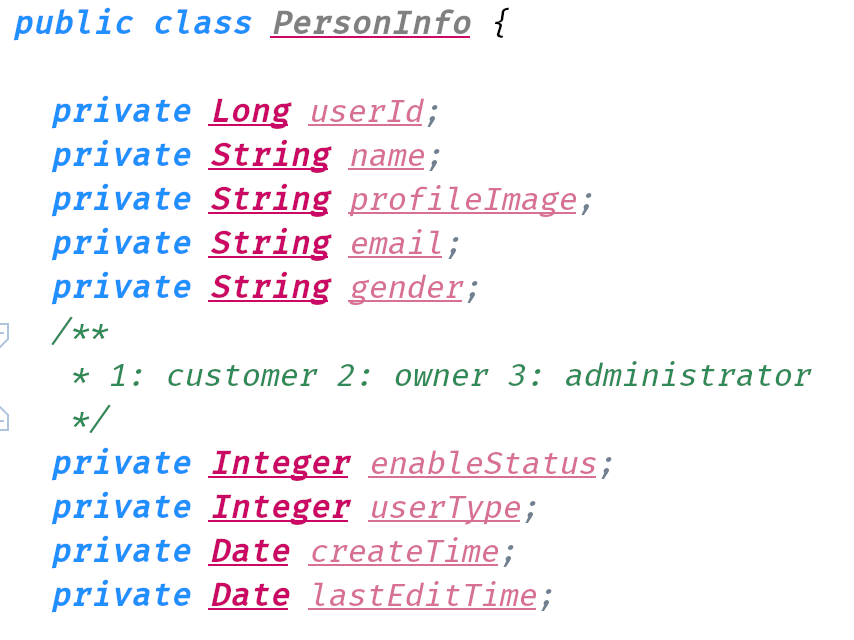
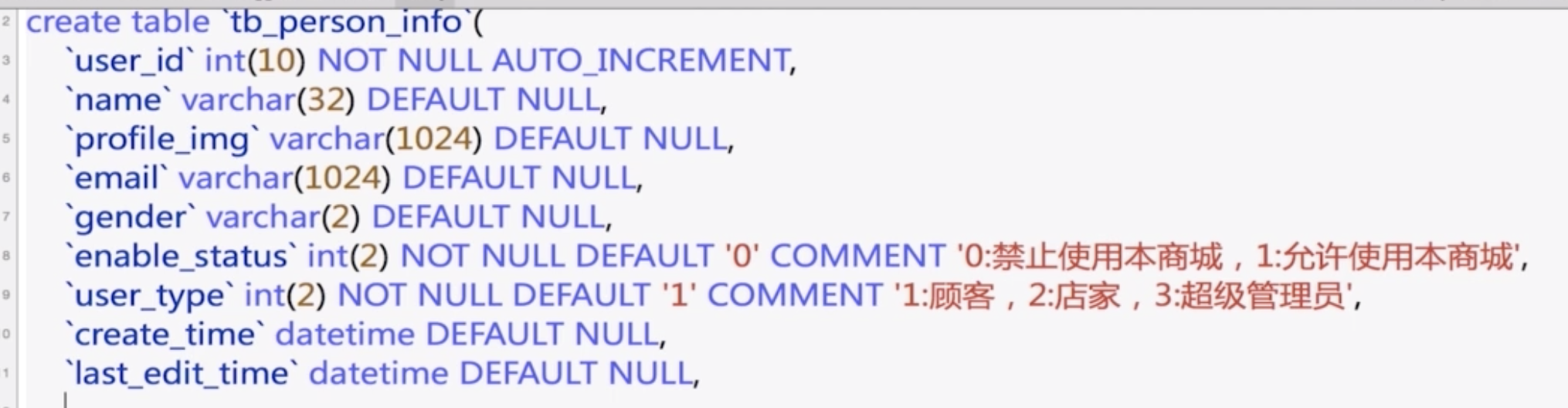
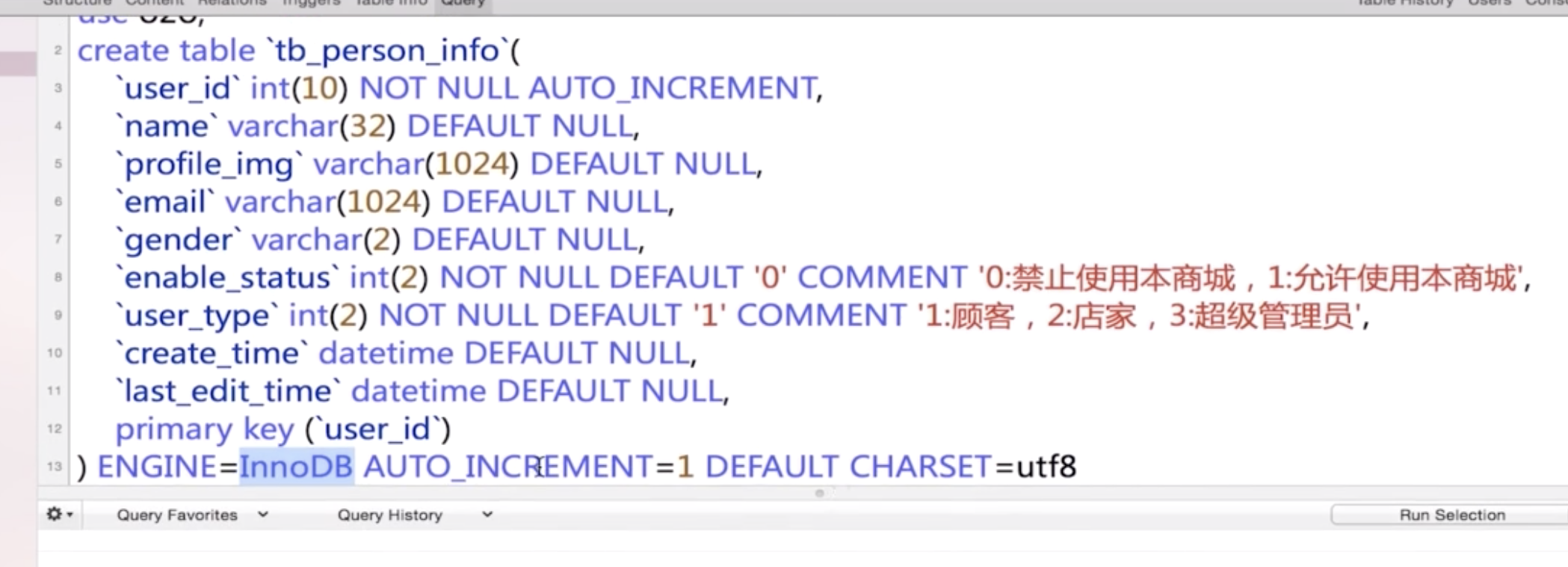
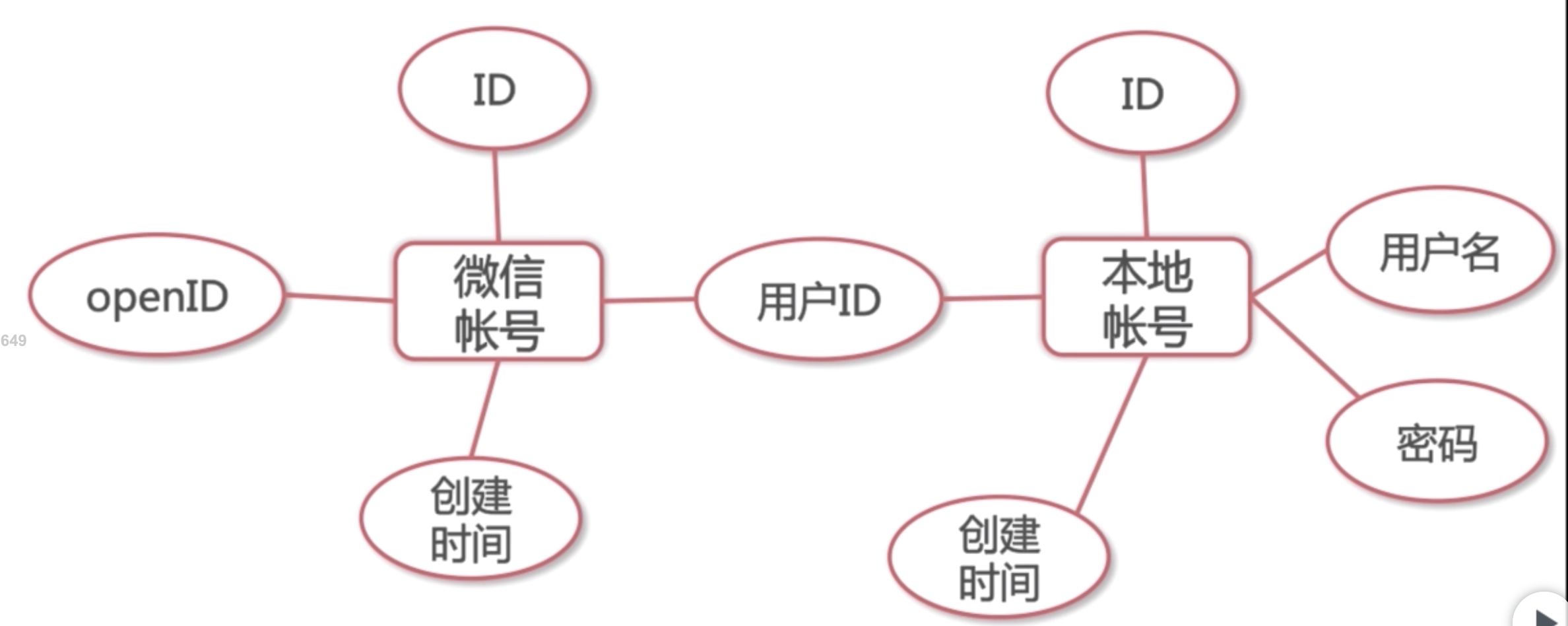
WechatAuth and LocalAuth


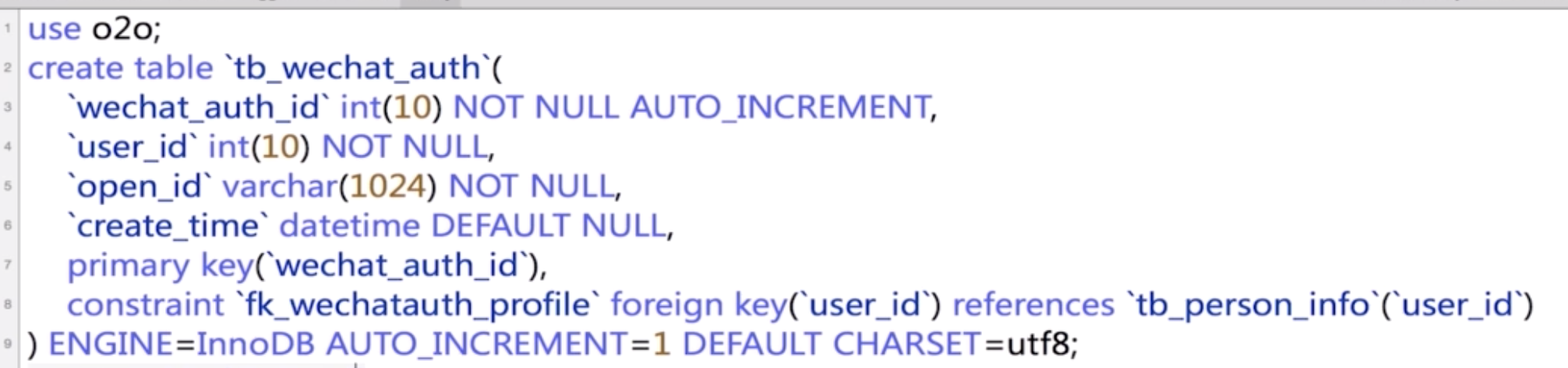


Here we should also change open_id in tb_wechat_auth into a unique key.
Q: Why do we want to set username to be unique?
A: Because we want to improve the performance of lookup.
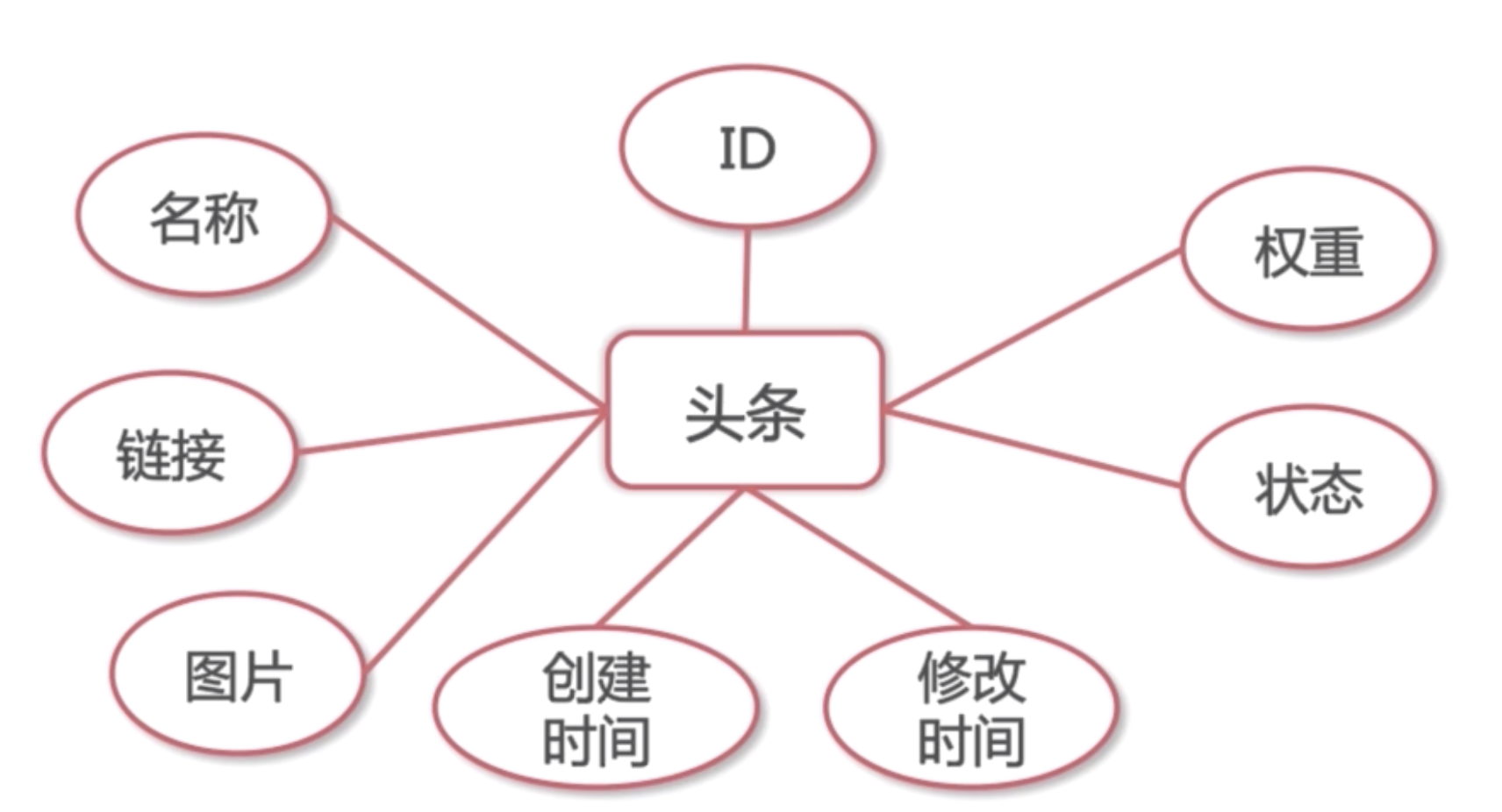
HeadLine

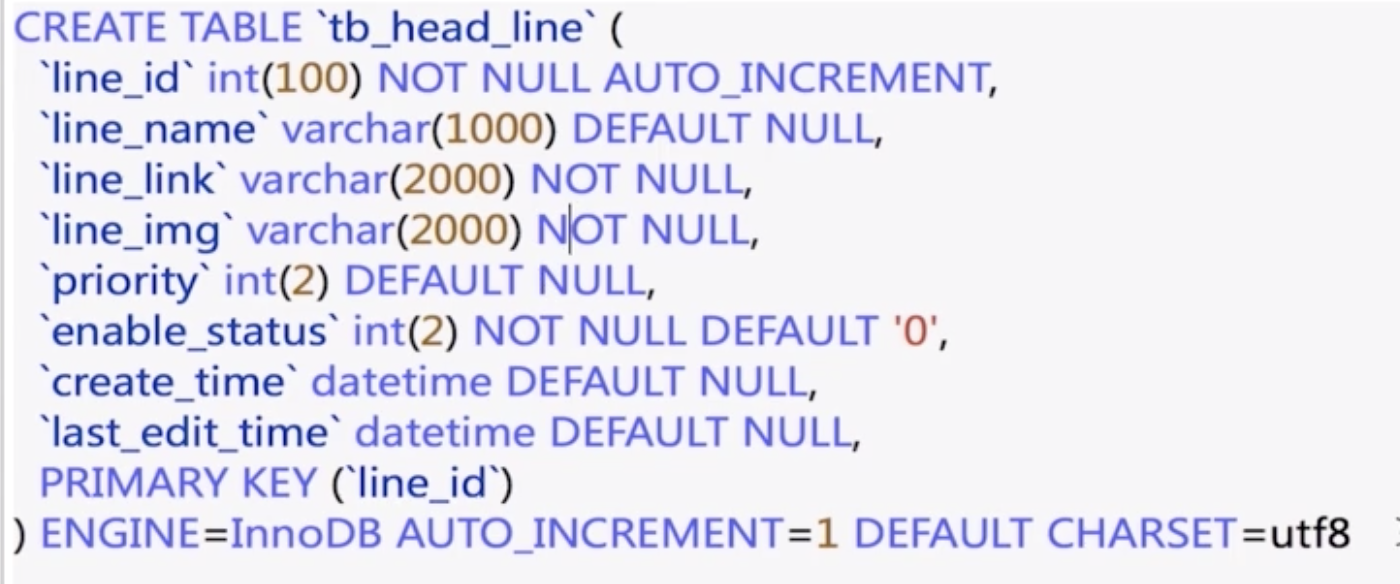
ShopCategory
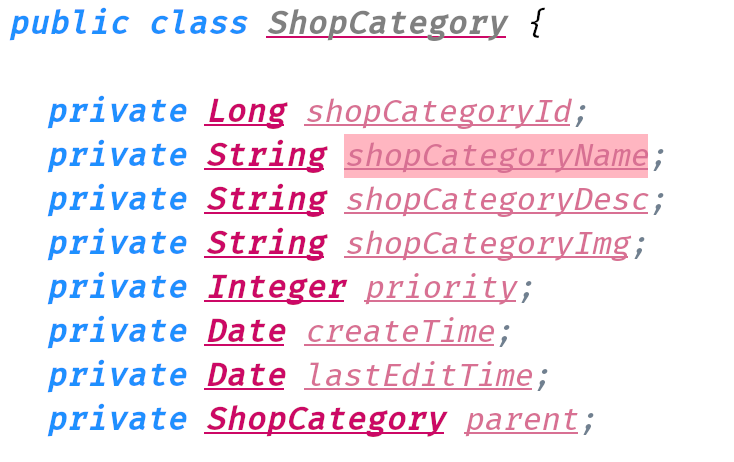

parentId is like a recurrence relation here. if the parent is null, that means the category is the root. Any child node can traverl all the way back to root.
Shop



ProductCategory


ProductImg


Product
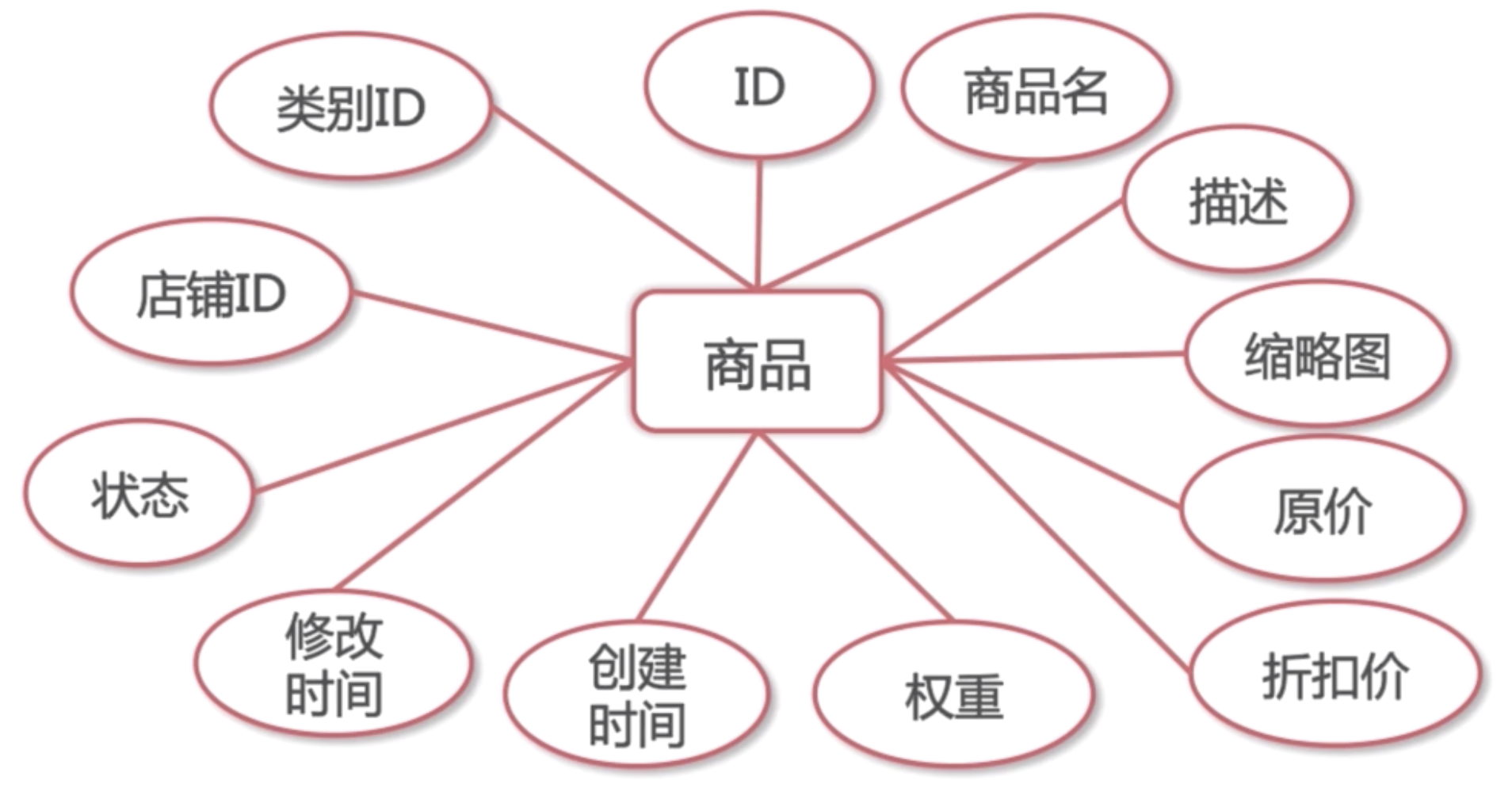



Configurations
Packages of the projects

Dependencies
- Junit
Has to be higher than 4.12, otherwise there’s error.
- Logback
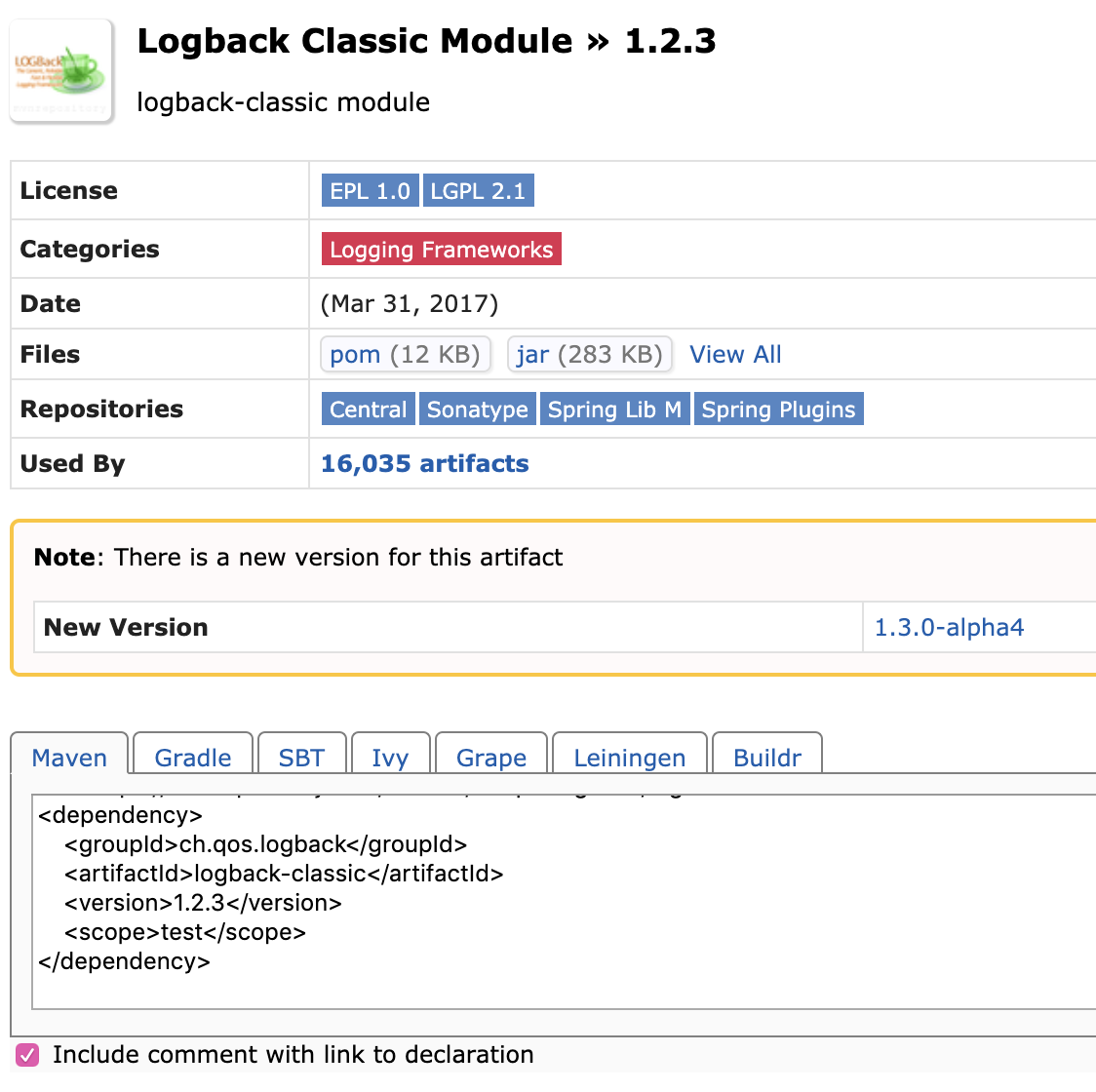
Here we want to remove \
test\ , since we also want it to appear in the actual scope.
spring
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58<properties>
<spring.version>4.3.7.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring -->
<!-- 1)包含Spring 框架基本的核心工具类。Spring 其它组件要都要使用到这个包里的类,是其它组件的基本核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 2)这个jar 文件是所有应用都要用到的,它包含访问配置文件、创建和管理bean 以及进行Inversion of Control
/ Dependency Injection(IoC/DI)操作相关的所有类。如果应用只需基本的IoC/DI 支持,引入spring-core.jar
及spring-beans.jar 文件就可以了。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 3)这个jar 文件为Spring 核心提供了大量扩展。可以找到使用Spring ApplicationContext特性时所需的全部类,JDNI
所需的全部类,instrumentation组件以及校验Validation 方面的相关类。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 4) 这个jar 文件包含对Spring 对JDBC 数据访问进行封装的所有类。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 5) 为JDBC、Hibernate、JDO、JPA等提供的一致的声明式和编程式事务管理。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 6)Spring web 包含Web应用开发时,用到Spring框架时所需的核心类,包括自动载入WebApplicationContext特性的类、Struts与JSF集成类、文件上传的支持类、Filter类和大量工具辅助类。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 7)包含SpringMVC框架相关的所有类。 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 8)Spring test 对JUNIT等测试框架的简单封装 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependencies>Servlet
Servlet serevice dependency1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- Servlet web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>json support for front-end
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- json解析 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.9</version>
</dependency>spring-core dependency
1
2
3
4
5
6<!-- Map工具类 对标准java Collection的扩展 spring-core.jar需commons-collections.jar -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
</dependency>mybatis dependency
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11<!-- DAO: MyBatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>mysql
mysql-connector-java supports sql api
com.mchange supports connection pool
1 | <!-- 数据库 --> |
1 | 什么是连接池 |
Configurations
jdbc
File name is jdbc.properties, save it under src/main/resources1
2
3
4jdbc.driver = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/o2o?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
jdbc.username = root
#jdbc.password = passwordmybatis
File name is mybatis-config.xml, save it under src/main/resources1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8<!-- 使用jdbc的getGeneratedKeys获取数据库自增主键值 -->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="true" />
<!-- 使用列标签替换列别名 默认:true -->
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true" />
<!-- 开启驼峰命名转换:Table{create_time} -> Entity{createTime} -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />spring
spring-dao.xml1
2
3
4
5<!-- 配置整合mybatis过程 -->
<!-- 1.配置数据库相关参数properties的属性:${url} -->
<!-- 2.配置连接池属性 -->
<!-- 3.配置SqlSessionFactory对象 -->
<!-- 4.配置扫描Dao接口包,动态实现Dao接口,注入到spring容器中 -->
spring-service.xml
1 | <!-- 扫描service包下所有使用注解的类型 --> |
spring-web.xml1
2
3
4
5<!-- 配置SpringMVC -->
<!-- 1.开启SpringMVC注解模式 -->
<!-- 2.静态资源默认servlet配置 (1)加入对静态资源的处理:js,gif,png (2)允许使用"/"做整体映射 -->
<!-- 3.定义视图解析器 -->
<!-- 4.扫描web相关的bean -->
web.xml
Integrate the configuration of Spring1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/spring-*.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring-dispatcher</servlet-name>
<!-- 默认匹配所有的请求 -->
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>Review

Test for DAO
Take Area class as an example, we try to implement its DAO.
Q: What is DAO?
A: DAO是Data Access Object数据访问接口,数据访问:顾名思义就是与数据库打交道。In computer software, a data access object (DAO) is an object that provides an abstract interface to some type of database or other persistence mechanism. By mapping application calls to the persistence layer, the DAO provides some specific data operations without exposing details of the database. This isolation supports the single responsibility principle. It separates what data access the application needs, in terms of domain-specific objects and data types (the public interface of the DAO), from how these needs can be satisfied with a specific DBMS, database schema, etc. (the implementation of the DAO).
We first implement the interface of user’s operation(such as insertion, deletion, update, query), and then map the DAO in the myBatis (mapper package) to the entity class. There we define the type of the operation and return type, then we can write SQLs to execute the actual queries.
Step:
- create interface AreaDao in o2o.dao
- create config file AreaDao.xml in resources.mapper
Here we don’t need to implement the actual AreaDao class but simply provide an interface is enough. MyBatis will do the job for us. We just need to map it to MyBatis.
- Specify the namespace, id, and resultType
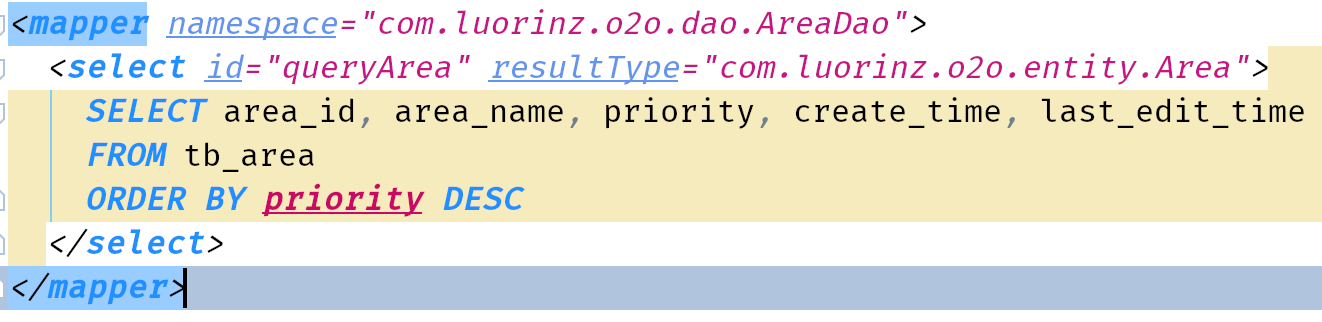
- Write the test for the dao.
First, create a BaseTest class in test/…/o2o/, which is used to initialize Spring and Junit configuration

@RunWith and @ContextConfiguratiion are often used together. First one indicate what test runner we want to use for junit. @ContextConfiguration indicates the Config file of Spring DAO.
Then create a concrete test class AreaDaoTest in ~/o2o.dao extending the BaseTest.

@Autowired is used to assemble the DAO class by Spring. Every time we declare an interface with @Autowired, Spring will automatically use its implementation class.
- Debug.
- in
jdbc.properties, password line cannot be omitted - jdbc.driver is deprecated, shoule be changed to
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver - Add
&serverTimezone=UTCto jdbc url - Make sure all paths are configured correctly.
Test for Service
- Create
AreaServiceinterface in service package, which has a getAreaList API. - Create
AreaServiceImplclass in service.impl package, create a DAO and implement the API. Just simply return the DAO’s queryArea() API.

Create
serevice.AreaServiceTestin test package, and add config file to the BaseTest.1
({"classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml", "classpath:spring/spring-service.xml"})
Same as testDao, test the getAreaList() API we defined in interface AreaService. Here we changed a way to test it. Notice that since we configure the mapper with AreaDao.xml, we know that the result return from the database is exactly the field we defined in entity class Area.

Test for Controller
- Since we use a super admin to control the Area, we create a superadmin package to manage related behaviour. Create
web.superadmin.AreaController. - Implement this class.
@Controller tag means this is an implementation class of Controller(just like @Service). Here we don’t have a Controller interface.
@RequestMapping means when we have a request calling superadmin, we direct it to our current class AreaController. Same as the following. Notice that we use lower case here for url.
@ResponseBody is used to write the data we have in controller to the body of response. Could be html, json or xml. In this case, we return json.
The reason why we use a Map<String, Object> here is because this data structure is like a json. We can put whatever we want as the value of a certain String, including error message.
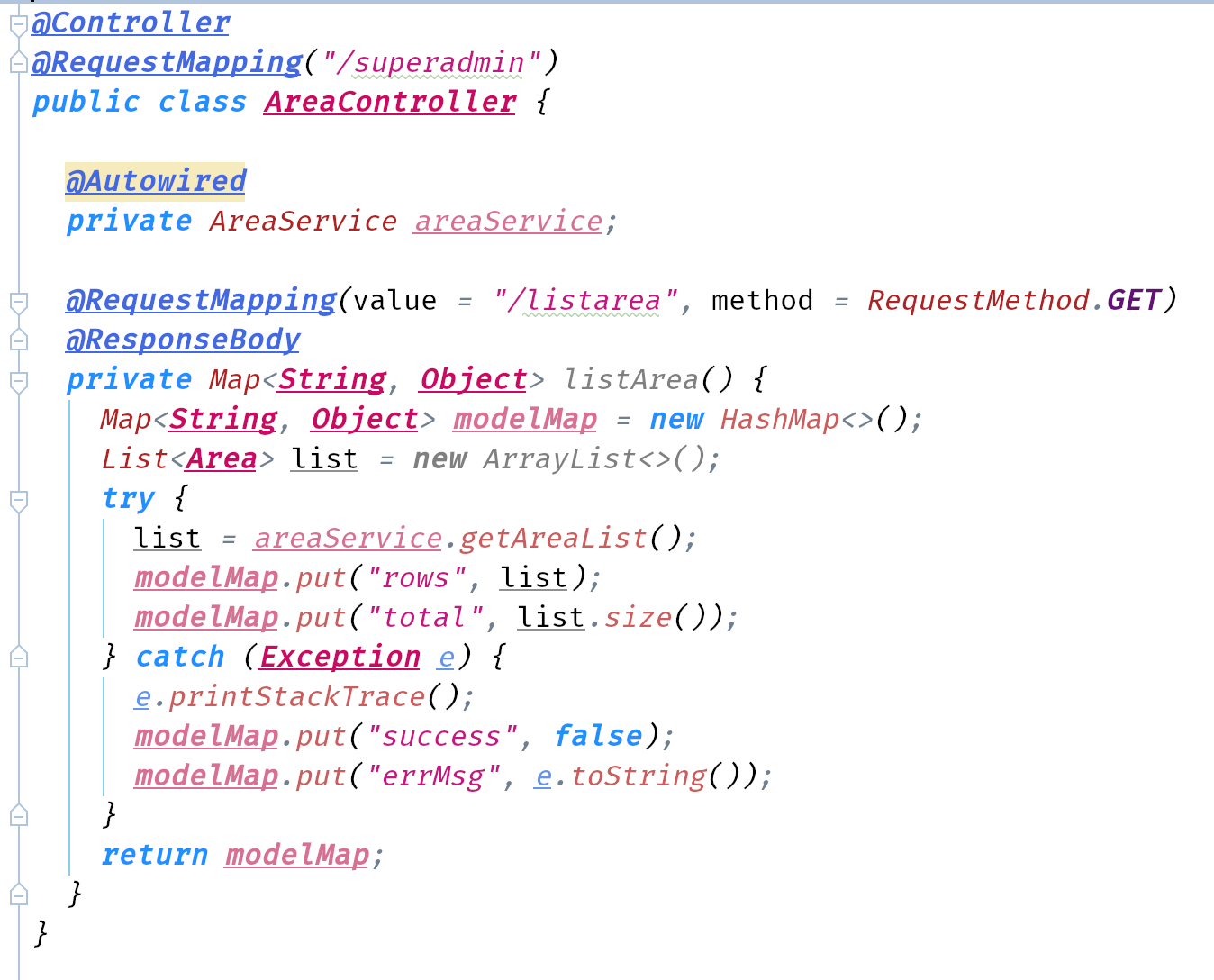
We can test it at http://localhost:8080/superadmin/listarea
and get something like
1 | {"total":2,"rows":[{"areaId":2,"areaName":"Chicago","priority":2,"createTime":null,"lastEditTime":null},{"areaId":1,"areaName":"Seattle","priority":1,"createTime":null,"lastEditTime":null}]} |
Debug: There’s a serious bug about bean multipartResolver. Annotate it will be fine.
Review
- Create the interface in DAO, and create certain APIs
- Create config file in mapper for this DAO, and Use SQL to execute operations on Database.
- Call DAO API in Service
- Call Service API in Controller and return it to front end(write to response).